From Crowdsourcing of ideas to Solutions Search.
Ideation platforms and open innovation platforms can respond quickly and effectively to a problem or to generation of new ideas through the reuse of knowledge or external ideas. The time saving and new opportunities brought by this approach attracts more and more companies.
Invented in the 2000’s and powered up in 2010, the open innovation platforms experience a constant growth as testified by the twofold increase of the number of challenges published every year.
The open innovation platforms manage the search and intermediation between seekers and solvers, organized around a specific topic (a challenge) similarly to other marketplaces.
Most often the intermediation is between a company and either individuals (ideas crowdsourcing ), or specialists involved in scientific research or with a particular expertise (search for solutions).
There are specific open innovation platforms models that involve e.g. students (Agorize) or start-ups (Club Open Innovation). The offers can be grouped in two categories:
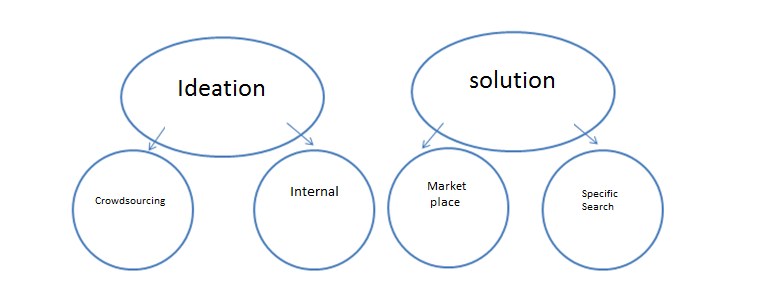
Fig.1: the different types of open innovation platforms
The ideation platforms aim at exploiting “collective intelligence”
Either with the largest audience, this we call “ideas crowdsourcing” (refer to Spigit, Agorize, Wazoku etc …) or towards certain communities e.g the employees of a company (refer to social intranet solutions as Jive)
Ideation platforms: the concept
These particular ideation platforms allow to restrict or enlarge the targeted public for example the consumers of a brand ; Coca-Cola, Oreo or Patagonia are heavy users who organize idea competitions to improve their products, their advertising campaigns etc…The idea selected gives birth to project and the inventor gets rewarded.
The solutions platforms search for the best experts
The solution platforms on the other hand, aim at solving a given problem. These open innovation platforms publicize a specific problem to a number of persons who are targeted as potentially being able to solve it. They have a function of intermediary and can provide an experts database, the project management and the option for the seeker to hide their identity.
We distinguish between two forms of solution platforms:
– the market places offer to experts the option to register themselves on their website and informs them when a challenge matches their skills
– the expert search platforms propose to identify the best experts of the domain of the question and to submit it to these experts specifically.
The open innovation platforms marketplaces (innocentive, innoget…) are relatively simple to set up but have to invest in their notoriety to create their expert database (200k to 400k for the biggest). It is difficult for them to be versatile or to qualify the actual expertise of their members.
The expert search open innovation platforms, instead, are more complex to implement as they require means to identify and contact experts (using data mining techniques). But they can be applied to any subject, ensure the relevance of those contacted and also ease the confidentiality management as challenges are not necessarily published on the web but sent directly to experts.
Facts and Figures
To better understand the activity of these open innovation platforms, let’s look at some key statistics (study based on public data from ideXlab, InnoCentive, Innoget and NineSigma).
A continuous growth of 100% per year
There is a growth of nearly 100% per year in the number of questions asked on open innovation platforms, with more than 500 in 2013 and a total of several thousands since their inception. Although this number is difficult to estimate, we think that about 5000 challenges were published by these players to date. This does not account for the challenges managed directly under the corporate brand with the help of intermediairies nor those that are confidential.
A significant increase of Challenges of smaller amount
Approximately 50% of challenges published on open innovation platforms include an explicit reward amount.
These prices have decreased by 25% per year over the last 3 years to reach an average value of € 20k in 2013. This decrease in average is largely dictated by the sharp increase of challenges with rewards below €10k. They represent half of the activity of open innovation platforms in 2013 but were inexistent in 2011. This follows a penetration of Open Innovation in more companies and product categories, including SMEs. Indeed, by making a more systematic use of open innovation platforms, companies are seeking for more solutions of smaller value. This is particularly true for Innocentive or ideXlab while NineSigma specializes in “grand challenges” worth hundreds of thousands to a million dollars.
Average resolution duration of 90 days
The average duration of a challenge is 90 days with a great variability depending on the open innovation platforms. Some favor the short time (~6 weeks) and other longer periods (24 weeks as Innoget). This difference is partly explained by the nature of the challenges. The requests for transfers of specific technology tend to be processed more quickly than broader requests for ideation.
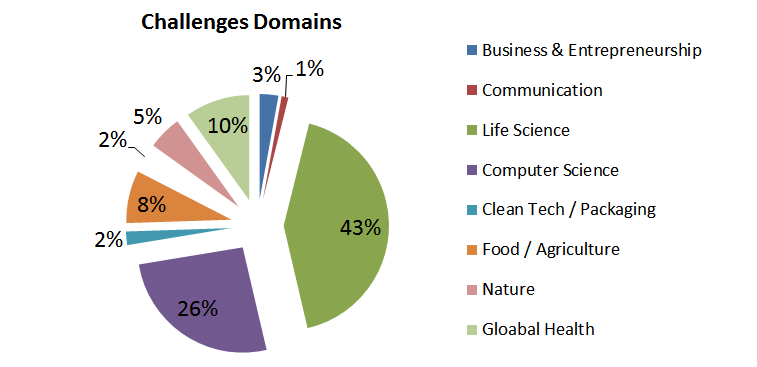
The life science and computer science are in the lead
There are specialized open innovation platforms such as in social development as Open Ideo or the acquisition of patents as Yet2.com and many others. So the domains covered are very broad but the main volume of requests is hosted by the generalist open innovation platforms.
Of these, the most requested areas are in order: the life sciences, IT and electronics that constitutes 70% of the total, far ahead of health or agriculture which probably demonstrate a lack of knowledge of these tools in some industry areas and so an great additional market potential.
Fig.2: breakdown of challenges by domains
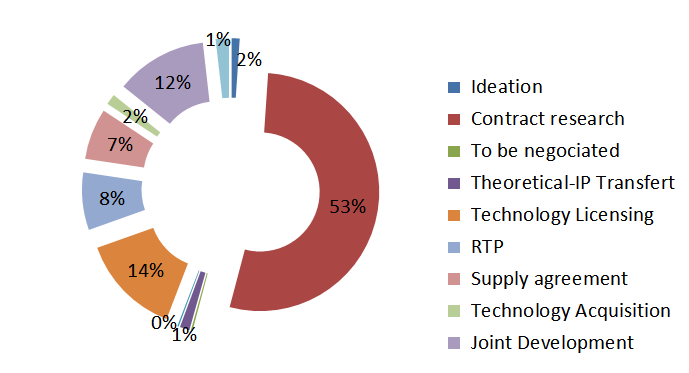
Contract research is the most popular collaboration format
The nature of partnerships varies depending on the maturity of the solution seeked, from theoretical ideation to actual supply agreements.
The most wanted category on open innovation platforms is contract research (53%), whereby a company enters into an agreement to finance the maturation or implementation of technology developped in previous research activities. This is a situation where the “innovation leverage ” is ideal as it benefits from existing knowledge and results while it still allows to acquire exclusive rights from the supplier at a reasonable cost. Next on list comes technology licensing (14 %) and joint developments.
Fig3: Breakdown by contract types
As a conclusion, let us note that the Open Innovation platforms offering is now well structured. The number of transactions has increased sharply in the past years and the practice is widely used for both large and smaller projects. However not all industry sectors have embraced Open Innovation yet and so there are promising untapped markets to enter into.









[…] Liévin is the founder of IdexLab, Open Innovation services consultancy, helping companies accelerate their transition towards a […]
[…] Liévin is the founder of IdexLab, Open Innovation services consultancy, helping companies accelerate their transition towards a […]
[…] Liévin is the founder of IdexLab, Open Innovation services consultancy, helping companies accelerate their transition towards a […]